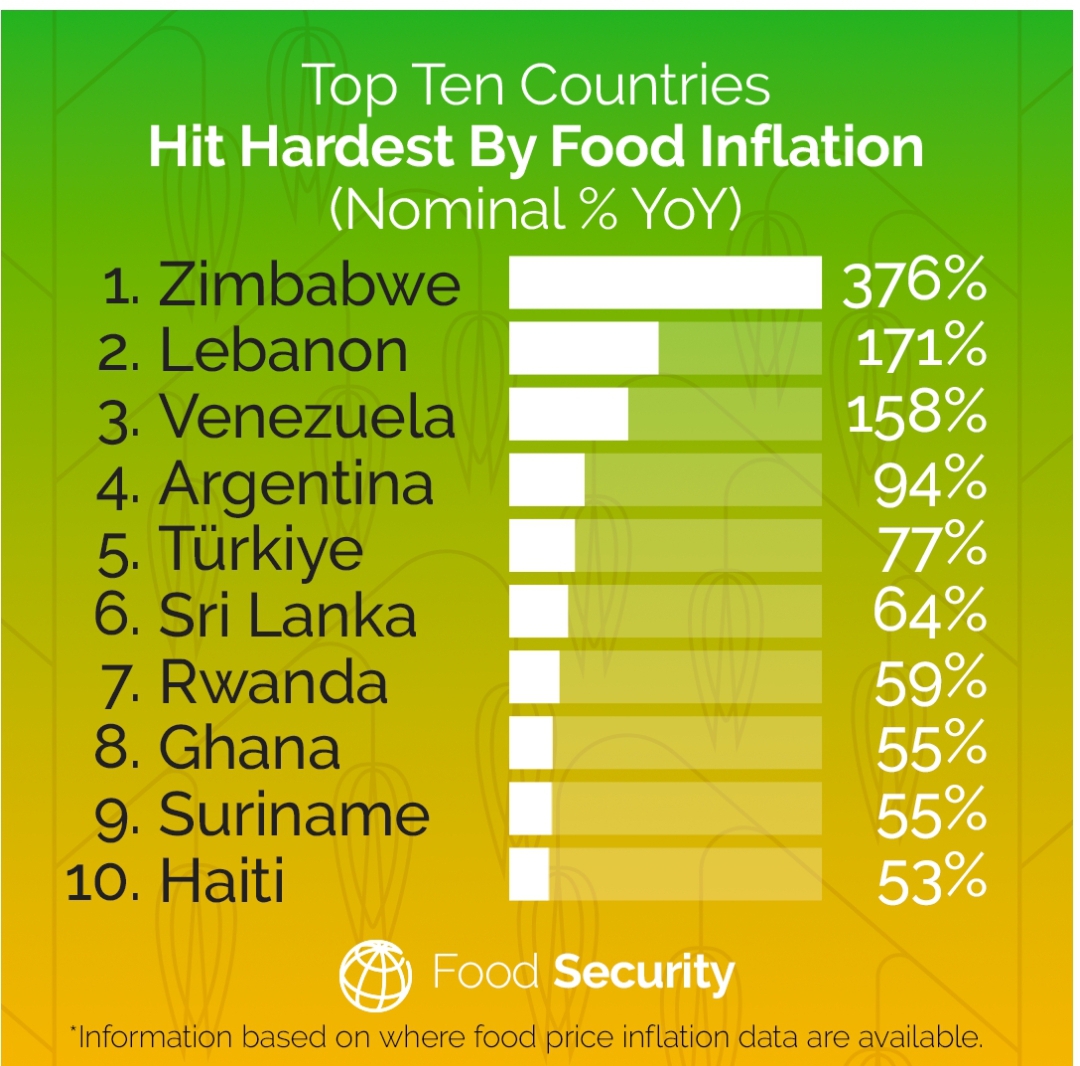
Domestic food price inflation remains high around the world. Information between September to December 2022 shows high inflation in almost all low-income and middle-income countries; 94.1% of low-income countries, 92.9% of lower-middle-income countries, and 89% of upper-middle-income countries have seen inflation levels above 5%, with many experiencing double-digit inflation.
The share of high-income countries with high food price inflation has risen to 87.3%. The countries affected most are in Africa, North America, Latin America, South Asia, Europe, and Central Asia.
Since the last update on December 13, 2022, agricultural, cereal, and export prices have remained relatively stable. The agricultural index closed at the same level, the export index 1% higher, and the cereal index 1% lower. Maize and wheat prices closed 1% and 2% lower, respectively, and rice prices 1% higher.
Maize and rice prices are 8% and 13% higher, respectively, than in January 2022, and wheat prices 2% lower. Maize and wheat prices are 27% and 13% higher, respectively, than in January 2021, and rice prices 10% lower. (See “pink sheet” data for agricultural commodity and food commodity prices indices, updated monthly.)
A December 2022 report released by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) has indicated that global food prices are expected to remain high because of war, energy costs, and weather events, despite interest rate hikes having slightly eased price pressures. Record prices have increased food insecurity, raised social tensions, and strained the budgets of countries that rely on food imports.
The 2022 Financing Flows and Food Crises Report released by the Global Network Against Food Crises highlights that countries that experience food crises receive the most humanitarian financing. When all sectors are considered, development allocations to food crisis countries are much larger than humanitarian assistance.
When considering allocations to countries based on drivers of food crises, countries where conflict and insecurity are the main drivers absorb the largest share of humanitarian and development assistance.
A recent World Bank blog underscored that high fertilizer prices have become a significant obstacle to food production in low income countries, destabilizing the 2023 and 2024 crop cycle; 205 million people are in acute food insecurity in 45 countries worldwide.
Many of these countries lack sufficient raw materials—nitrogen, potash, phosphate, natural gas—and production facilities to ensure that farmers can affordably access fertilizers. The challenge is clearest in Sub-Saharan Africa, where disruptions to fertilizer exports from Belarus and Russia and restrictions of other exporting countries have hit poor households hardest.
Fertilizer prices have tripled since early 2020 and remain volatile, preventing smallholder farmers from accessing a stable supply. Meanwhile, farmers in more-advanced economies can afford to plant more and purchase fertilizer because they benefit from subsidies that often cover natural gas for fertilizer and diesel fuel for equipment.
A new analysis conducted by IFPRI of 1.27 million children in 44 low- and middle-income countries explores the potential impacts of food inflation on wasting and stunting among 1.27 million pre-school children.
The study demonstrates that the impacts of food inflation strike early—in the first 1,000 days of life—and during pregnancy and infancy and disproportionately affect the rural poor and landless. As such, there is an urgent need to improve women’s nutrition and health before and during pregnancy to guarantee prenatal health and nutrition support for mothers and children.
Following the start of the war in Ukraine, trade-related policies imposed by countries have surged. The global food crisis has been partially made worse by the growing number of food trade restrictions put in place by countries with a goal of increasing domestic supply and reducing prices. As of December 2022, 19 countries have implemented 23 food export bans, and eight have implemented 12 export-limiting measures.
World Bank Action
As part of a comprehensive, global response to the food security crisis, in May 2022 the World Bank announced that it is making up to $30 billion available over a period of 15 months, including $12 billion in new projects.
From April through September, the Bank has committed $8.1 billion for new projects across 47 countries – most of this support is in Africa, which is one of the hardest hit regions by the food crisis. This financing will include efforts to encourage food and fertilizer production, enhance food systems, facilitate greater trade, and support vulnerable households and producers such as:
A $125 million project in Jordan aims to strengthen the development the agriculture sector by enhancing its climate resilience, increasing competitiveness and inclusion, and ensuring medium- to long-term food security.
A $300 million project in Bolivia that will contribute to increasing food security, market access and the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices.
A $315 million loan to support Chad, Ghana and Sierra Leone to increase their preparedness against food insecurity and to improve the resilience of their food systems.
A $500 million Emergency Food Security and Resilience Support Project to bolster Egypt’s efforts to ensure that poor and vulnerable households have uninterrupted access to bread, help strengthen the country’s resilience to food crises, and support to reforms that will help improve nutritional outcomes.
A $130 million loan for Tunisia, seeking to lessen the impact of the Ukraine war by financing vital soft wheat imports and providing emergency support to cover barley imports for dairy production and seeds for smallholder farmers for the upcoming planting season.
The $2.3 billion Food Systems Resilience Program for Eastern and Southern Africa, helps countries in Eastern and Southern Africa increase the resilience of the region’s food systems and ability to tackle growing food insecurity. The program will enhance inter-agency food crisis response also boost medium- and long-term efforts for resilient agricultural production, sustainable development of natural resources, expanded market access, and a greater focus on food systems resilience in policymaking.
In May, the World Bank Group and the G7 Presidency co-convened the Global Alliance for Food Security, which aims to catalyze an immediate and concerted response to the unfolding global hunger crisis. The Alliance has developed the publicly accessible Global Food and Nutrition Security Dashboard, which provides timely information for global and local decision-makers to help improve coordination of the policy and financial response to the food crisis.
The heads of the FAO, IMF, World Bank Group, WFP, and WTO released a Second Joint Statement on the Global Food Security and Nutrition Crisis, which notes that considerable progress has been made in the four key areas: providing immediate support to the vulnerable, facilitating trade and the international supply of food, boosting production, and investing in climate-resilient agriculture.
Last Updated: Jan 17, 2023




thanks for info
What are the main factors contributing to the current high domestic food price inflation globally?
What are the potential long-term consequences of sustained high food prices on global food security?